Written by: Igor
Published: December 2025
Machine learning in manufacturing isn't a futuristic concept anymore-it's a practical tool that turns your factory data into a competitive advantage. It uses smart algorithms that learn from your production data to predict equipment failures, automate quality checks, and fine-tune your supply chain. This guide will show you how to move from theory to practical, on-the-floor implementation that delivers a clear return on investment.
Snapshot: key takeaways
- Start small: Don't try to overhaul your entire factory. Pick one high-impact, low-complexity problem for a pilot project, like predicting failure on a single bottleneck machine.
- Focus on business outcomes: Translate technical wins into dollars and cents. Measure success with KPIs like Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and scrap rate reduction.
- Data quality is everything: The rule is simple: garbage in, garbage out. Your model's predictions are only as good as the data it's trained on. A data audit is a non-negotiable first step.
- Get operator buy-in: A perfect model that no one uses is worthless. Involve your maintenance and operations teams from day one to ensure the solution is trusted and adopted on the factory floor.
Why machine learning is a competitive necessity

If you're staring at production reports wondering how competitors keep pulling ahead, the answer isn't about working harder-it’s about working smarter. The gap between market leaders and everyone else is widening, and the difference is data. While traditional manufacturing is stuck in reactive fixes, smart factories use machine learning to get ahead of issues before they hit the bottom line.
This shift has turned machine learning in manufacturing from an industry buzzword into a critical tool for survival. It’s about making proactive, data-driven decisions instead of relying on gut feelings.
The market numbers tell the same story. The global AI in manufacturing market is projected to hit nearly $17 billion by 2027, according to a report from MarketsandMarkets. Early adopters are already reaping huge rewards. According to McKinsey, companies that successfully scale AI can add up to 122% more cash flow. You can find more machine learning statistics and insights here.
This guide cuts through the noise and gets straight to the practical applications that are delivering real return on investment (ROI) right now. You will learn how to:
- Prevent costly downtime with predictive maintenance models.
- Improve product quality using computer vision systems.
- Optimize your supply chain by forecasting demand more accurately.
- Increase production yield by pinpointing hidden inefficiencies.
Core machine learning applications on the factory floor
Let's break down the four most common applications that founders and operators are using right now to get a competitive edge.
Predictive maintenance: a smart check engine light
Think of predictive maintenance as a hyper-intelligent check engine light for your most vital machinery. It doesn't just tell you something is wrong-it warns you weeks in advance about what is likely to fail.
This is a massive leap from reactive maintenance (fixing things after they break) and even preventive maintenance (fixing things on a schedule, needed or not).
Machine learning models analyze real-time data from Internet of Things (IoT) sensors on your equipment. They listen for tiny shifts in vibration, temperature, and acoustic signals invisible to human operators. The algorithm learns the "healthy" signature of each machine and flags any deviation as a future failure.
This approach turns maintenance from a cost center into a strategic operation. Smart manufacturing initiatives, driven by ML, are delivering 10-20% gains in production output and a 7-20% bump in employee productivity. You can get more details on these smart manufacturing trends on NetSuite.com.
AI-powered quality control: a tireless inspector
Human quality inspection is crucial, but it’s prone to fatigue and inconsistency. An inspector can't spot microscopic defects on a high-speed production line. This is where AI-powered quality control, mainly using computer vision, changes the game.
High-resolution cameras mounted over the assembly line capture images of every product. A trained machine learning model analyzes these images in milliseconds, comparing each one against a "golden standard" of a perfect product.
It can instantly identify subtle defects like:
- Micro-scratches on a polished metal surface.
- Slight color deviations in a plastic part.
- Missing components in a complex electronic assembly.
This isn't just about catching more defects. It's about catching them instantly, slashing scrap rates and making sure a faulty product never leaves the factory. For a deeper dive on how real-time data can stabilize factory operations, check out this piece on leveraging Simulation and IoT to Mitigate Risk.
Supply chain and inventory optimization
Your supply chain is a complex web. One disruption can lead to costly stockouts or wasteful overstock. Machine learning brings a new level of intelligence to demand forecasting and inventory management.
Instead of just looking at historical sales, ML models analyze a wider set of variables. They digest market trends, competitor pricing, and even weather patterns to produce far more accurate demand forecasts.
This means your factory produces what the market actually wants, when it wants it. It avoids tying up capital in excess inventory and minimizes the risk of lost sales. The result is a leaner, more resilient supply chain.
Process and yield optimization
Finally, machine learning can act as a powerful optimization engine for your entire production process. Even efficient factories have hidden inefficiencies that add up to significant losses.
ML algorithms dig through massive amounts of production data to find hidden patterns. The model might discover that slightly adjusting a machine's temperature by two degrees could boost throughput by 5% while cutting energy use.
These are the kinds of multi-variable connections nearly impossible for a human to spot. By continuously learning, the system can recommend ongoing adjustments to maximize your yield, reduce waste, and improve your Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) score.
Building your data and infrastructure foundation
Machine learning models are brilliant, but they’re useless without the right fuel: data. Before you can predict equipment failures, you need a solid foundation of clean, reliable data and the right infrastructure.
Remember the golden rule of data science: garbage in, garbage out. The quality of your ML model's predictions is directly tied to the quality of the data it learns from.
The fuel: what data do you really need?
Your factory is a goldmine of data. The trick is to collect and organize it with a clear purpose. For most manufacturing use cases, you’ll focus on three main data types.
- Sensor and machine data: This is the lifeblood for predictive maintenance-real-time streams of vibration, temperature, pressure, and motor speed.
- Production and quality data: This includes production logs, error codes, and images from inspection cameras. This helps models understand the difference between a "good" and a "bad" product.
- Operational data: This covers broader context like work orders, maintenance records, and inventory levels. It's crucial for connecting machine performance to business outcomes.
Getting this data into one place is often the first hurdle. A good first step is a thorough audit of your current data landscape-a core part of any AI readiness assessment. You can learn more in our guide on how to conduct an AI readiness assessment.
The engine: the infrastructure that powers ml
Once you have the fuel, you need an engine. Your infrastructure comes down to three key pieces: collection, storage, and compute.
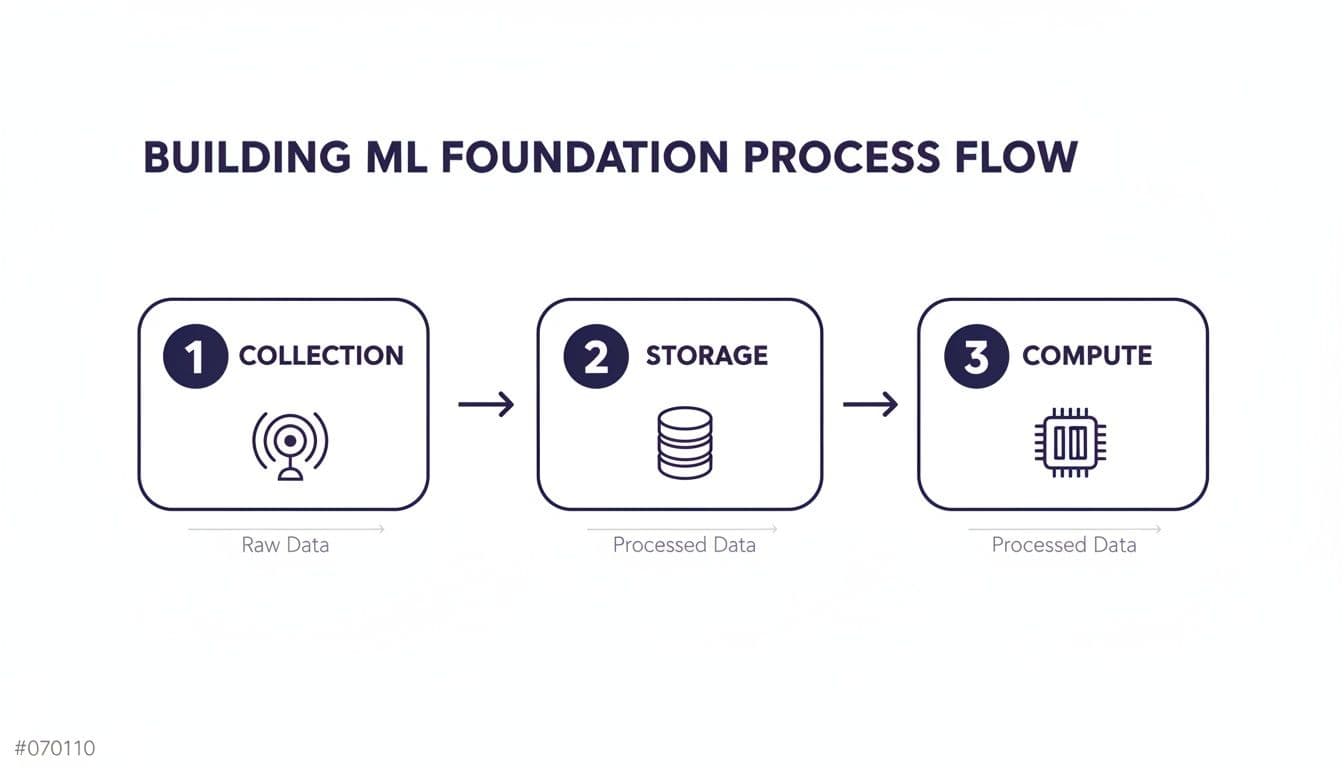
Data collection starts with IoT sensors. That data then needs a home, and you have two main choices.
- On-premise: Storing data on your own physical servers. This gives you total control but comes with high upfront costs and ongoing maintenance.
- Cloud: Using a provider like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure. This is far more flexible and scalable, letting you pay only for what you use. For most companies, the cloud is the clear winner.
Training a machine learning model is an incredibly demanding job. For the heavy lifting, you need a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). GPUs can slash model training time from weeks to hours. Cloud platforms let you "rent" access to world-class GPUs, giving you immense power without buying expensive hardware.
Your roadmap from pilot project to full-scale deployment
Jumping into machine learning isn’t like flipping a switch. The smarter play is a phased rollout that proves its value at every step.
Phase 1: the quick-win pilot project
Your first project sets the tone. The goal is simple: pick a high-impact, low-complexity problem and deliver a measurable win-fast. This is not the time to boil the ocean.
A perfect candidate? Predicting failures on a single, critical machine that’s a known bottleneck. The scope is tight, the data is usually there, and the business impact is easy to calculate.
To nail down the right pilot, use these criteria:
- Solve a real pain point: Go after a problem that keeps your operations team up at night.
- Check your data: Do you have at least six to twelve months of relevant historical data?
- Define success upfront: Define success in concrete business terms, like "reduce unplanned downtime on CNC Mill #3 by 15% within three months."
Here's a simple checklist to help you choose:
- [ ] High business impact: Will solving this problem save significant money or time?
- [ ] Good data available: Is the necessary historical data clean and accessible?
- [ ] Low implementation complexity: Can a small team tackle this in under 3 months?
- [ ] Clear success metric: Can you define a single number (e.g., % downtime reduction) to measure success?
This framework forces you to think critically about where to place your first bet.
Phase 2: building and training the model
With a clear target, it’s time to build. This is where your data scientists and engineers work, but operators need to stay in the loop-their domain expertise is gold.
Think of it like teaching an apprentice. You show the model thousands of historical examples, pointing out which patterns led to a failure and which didn't. Over time, it learns to spot the subtle warning signs.
The key is getting continuous feedback from your maintenance crew to make sure the model’s "lessons" match reality. Getting this stage right is often one of the biggest AI implementation challenges manufacturers face.
Phase 3: deployment and continuous monitoring
A trained model on a laptop is useless. Deployment is where you integrate its predictions into your team's daily workflow. This could be as simple as an automated alert on a maintenance manager's dashboard.
But the job isn’t done. You have to watch the model’s performance. Its accuracy can degrade over time as equipment ages or processes shift. This is known as model drift.
Constant monitoring helps you catch this drift early, so you can retrain the model with fresh data. Adopting solid MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) practices is non-negotiable here. You can learn more about these in this guide to 10 Actionable MLOps Best Practices for Production AI.
Phase 4: scaling up success
Once your pilot project delivers ROI, you have a powerful success story. Now you scale. The framework is simple: find the next most critical bottleneck and run the same playbook.
Scaling doesn't mean just copying the same model everywhere. Each machine has its own unique data signature. But the process, the infrastructure, and the lessons learned can be replicated much faster for every project that follows. This methodical approach is how you turn an initial quick win into a factory-wide intelligence engine.
Measuring success and avoiding common pitfalls
Bringing machine learning into a manufacturing plant is about driving measurable business results. True success is defined by the impact on the metrics that matter to your bottom line.
Key performance indicators that matter
Your machine learning solution's success should be obvious in the metrics you already use. Keep a close eye on these KPIs:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): A good ML model should boost your OEE score by increasing availability (less downtime), performance (higher throughput), and quality (fewer defects).
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): For predictive maintenance, this is your north star. A successful model will stretch out the average time equipment runs between issues.
- Scrap rate reduction: AI-powered quality control needs to lead to a direct, measurable drop in the percentage of products you scrap.
Navigating common implementation pitfalls
Many promising ML projects fail. The failures are almost never about the tech itself-they’re about flawed strategy.
- Choosing technology before the problem: This is the most common mistake. A team gets excited about a new algorithm without first locking down a high-value business problem. Actionable tip: Start with the pain. Ask your operations team to name their single biggest bottleneck.
- Ignoring data quality issues: "Garbage in, garbage out" is the absolute law. If you train a model on messy data, it will spit out unreliable predictions. Actionable tip: Run a full data audit before writing any code. Our guide on how to implement AI in business can give you a framework for this.
- Failing to get operator buy-in: A perfect model that no one trusts is worthless. Actionable tip: Bring your floor team into the project from day one. Their feedback is gold for training a model that understands real-world conditions.
Your next step into smart manufacturing
Getting started with machine learning in manufacturing is a marathon, not a sprint. We’ve walked through how to find high-impact problems, build a solid data foundation, and launch a pilot project that delivers value. Your next move is to pinpoint one critical business problem that your existing data could help solve.
Focus on a single, well-defined goal, like cutting downtime on one bottleneck machine. Start there, score a clear win, and use that success to build momentum. This is how you bring machine learning in manufacturing to life. It's a focused, step-by-step approach that unlocks a smarter, more competitive production floor.
We at N² labs can help you find that high-impact pilot project and build a practical roadmap for weaving machine learning into your operations. Let's talk about turning your factory data into a real competitive advantage.
FAQ
The biggest roadblock is almost always the state of your data. Most manufacturers find their data is locked in different systems or "silos," making it difficult to get a unified view. A huge chunk of any initial project is just centralizing, cleaning, and prepping this data. This is why starting with a small pilot where you know the data is relatively clean is so effective.
Costs vary widely. A focused pilot project might run into the tens of thousands of dollars, while a full-scale factory overhaul could cost millions. The main cost drivers are data infrastructure, specialized talent, and cloud computing services. However, a good pilot is designed to deliver a positive ROI quickly. Preventing just one catastrophic equipment failure can often pay for the entire project.
Not right away. For a first project, it's often smarter and more cost-effective to work with a specialized consultancy or use a managed AI/ML platform. This lets you prove the value of machine learning in manufacturing without the massive overhead of building an in-house team from scratch. Once you have a successful pilot and a clear roadmap, you can think about building your own team.
AI quality control using computer vision offers a few game-changing advantages. First, accuracy-AI can spot microscopic defects invisible to the human eye. Second, consistency-an AI system performs at the same high level 24/7 without fatigue. Finally, it provides actionable insights by generating detailed data on defect types and frequencies, helping you fix the root cause of quality issues for good.